Build-up of radon in homes is a health concern and many lung cancer cases are attributed to radon exposure each year. About 12% of lung cancers and more than 20,000 Americans die of radon-related lung cancer each year. The Surgeon General of the United States has issued a Health Advisory warning Americans about the health risk from exposure to radon in indoor air. Dr. Carmona, the Nation’s Chief Physician urged Americans to test their homes to find out how much radon they might be breathing. He also stressed the need to remedy the problem as soon as possible.
You cannot see, smell, or taste radon. But it still may be a problem in your home. When you breathe air containing radon, you increase your risk of getting lung cancer. In fact, the Surgeon General of the United States has warned that radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States today. If you smoke and your home has high radon levels, your risk of lung cancer is especially high.
Radon Testing
Radon Testing is the only way to find out your home’s radon levels. EPA and the Surgeon General recommend testing all homes below the third floor for radon. If you find that you have high radon levels, there are ways to fix a radon problem. Even very high levels can be reduced to acceptable levels. Radon has been found in homes all over the United States. It comes from the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rock and water and gets into the air you breathe. Radon typically moves up through the ground to the air above and into your home through cracks and other holes in the foundation. Radon can also enter your home through well water. Your home can trap radon inside.
Any home can have a radon problem. This means new and old homes, well-sealed and drafty homes, and homes with or without basements. In fact, you and your family are most likely to get your greatest radiation exposure at home. That is where you spend most of your time. Nearly 1 out of every 15 homes in the United States is estimated to have an elevated radon level. Elevated levels of radon gas have been found in homes in your state.
If your home has not yet been tested for Radon have a test taken as soon as possible. If you can, test your home before putting it on the market. You should test in the lowest level of the home which is suitable for occupancy. This means testing in the lowest level that you currently live in or a lower level not currently used, but which a buyer could use for living space without renovations.
Frequently Asked Questions

Q: What is radon, and why should I care?
A: Radon, is the second leading cause of lung cancer, and the first leading cause among non-smokers. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as a decay product of radium. Radon comes from the ground, and is everywhere in our atmosphere. However, its concentration can vary widely in buildings where it can build up in the interior air. For more info on radon gas, read the Wikipedia page here.
Q: There is a unit on my property that says “Radalink” on it. What’s going on?
A: It is possible that your property is being tested for radon gas by your property inspector. Please do not touch or move the unit, or change the closed house conditions of your property. That is, do not change the status of heating or air conditioning, and do not open doors or windows, except to enter or exit quickly from the first floor doors. Contact your property inspector if you have additional questions about the status of your radon test.
Q: Does the monitor emit radiation or anything harmful?
A: Our monitors only take readings and do not emit any radiation or chemicals, and are in no way harmful to people or pets.
Q: What exactly does the Radalink radon monitor record?
A: Our monitors record radon concentration, temperature, barometric pressure, and relative humidity once per hour for the duration of the test. Our monitors also have a sensor that detects if the monitor has been moved during a test.
Q: Can we open our windows during the test?
A: All doors and all windows on all levels of the house must be kept closed, except for normal entry and exit through first floor doors. Heating and air conditioning equipment should operate normally. Window or wall mounted air conditioners may be used if the fresh air damper is set to the closed position. Fireplaces and wood stoves may not be used unless they are the primary heat source for the house. Whole house fans may not be used during the test.
Q: How long does the radon test last?
A: Tests take a minimum of 48 hours to complete. Radalink radon monitors can collect data for up to 5 days.
Q: Our radon test came back at over 4.0 pC/l. Should we be concerned?
A: Any radon level above the EPA recommended safe limit of 4.0 pC/l can be mitigated with a radon reduction system. These systems are not complicated or expensive. So, there should be no need for major concern if this involves a property being prepared for sale. But, after a mitigation system is installed, the radon levels should be tested again to make sure that the system is effectlively keeping the radon level below the EPA recommended safe limit.
Q: How much does it cost to have my property tested for radon?
A: Radon test costs can vary, depending on the size of the property, the state requirements of the testing process, and the pricing offered by the inspector that you hire to conduct the test. Typically prices range from $75 to $250 per test.
Radon Myths and Facts
MYTH: Scientists are not sure that radon really is a problem.
FACT: Although some scientists dispute the precise number of deaths due to radon, all the major health organizations (like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the American Lung Association and the American Medical Association) agree with estimates that radon causes thousands of preventable lung cancer deaths every year. This is especially true among smokers, since the risk to smokers is much greater than to non-smokers.
MYTH: Radon testing is difficult, time-consuming and expensive.
FACT: Radon testing is easy and inexpensive.
MYTH: Radon testing devices are not reliable and are difficult to find.
FACT: Reliable testing devices are available from qualified radon testers and companies.
MYTH: Homes with radon problems can’t be fixed.
FACT: There are simple solutions to radon problems in homes. Hundreds of thousands of homeowners have already fixed radon problems in their homes. Radon levels can be readily lowered for $800 to $2,500 (with an average cost of $1,200)..
MYTH: Radon affects only certain kinds of homes.
FACT: House construction can affect radon levels. However, radon can be a problem in homes of all types: old homes, new homes, drafty homes, insulated homes, homes with basements, and homes without basements. Local geology, construction materials, and how the home was built are among the factors that can affect radon levels in homes.
MYTH: Radon is only a problem in certain parts of the country. 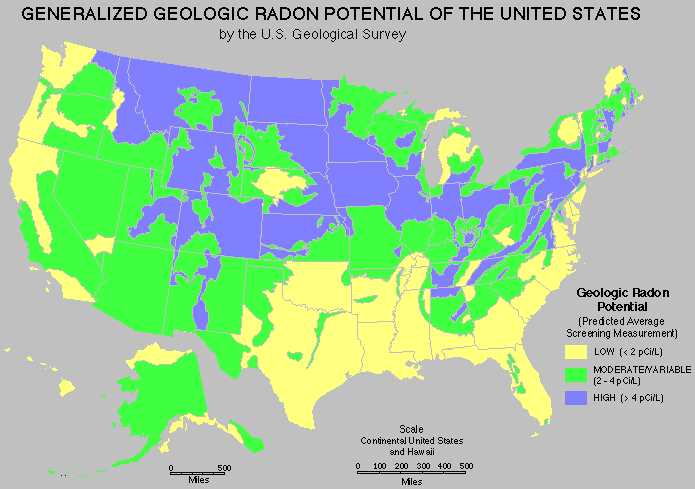
FACT: High radon levels have been found in every state. Radon problems do vary from area to area, but the only way to know your radon level is to test.
MYTH: A neighbor’s test result is a good indication of whether your home has a problem.
FACT: It’s not. Radon levels can vary greatly from home to home. The only way to know if your home has a radon problem is to test it.
MYTH: It’s difficult to sell homes where radon problems have been discovered.
FACT: Where radon problems have been fixed, home sales have not been blocked or frustrated. The added protection is some times a good selling point.
MYTH: I’ve lived in my home for so long, it doesn’t make sense to take action now.
FACT: You will reduce your risk of lung cancer when you reduce radon levels, even if you’ve lived with a radon problem for a long time.
MYTH: Short-term tests can’t be used for making a decision about whether to fix your home.
FACT: A short-term test, followed by a second short-term test* can be used to decide whether to fix your home. However, the closer the average of your two short-term tests is to 4 pCi/L, the less certain you can be about whether your year-round average is above or below that level. Keep in mind that radon levels below 4 pCi/L still pose some risk. Radon levels can be reduced in most homes to 2 pCi/L or below.
